|
| Mesoscale All-Atom Influenza Virus Simulations Suggest New Substrate Binding Mechanism |
|
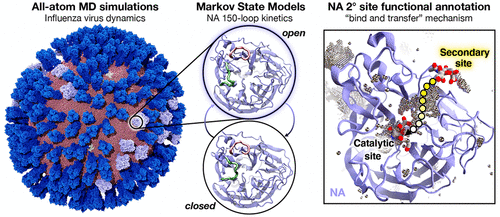
Influenza virus circulates in human, avian, and swine hosts, causing seasonal epidemic and occasional pandemic outbreaks. Influenza neuraminidase, a viral surface glycoprotein, has two sialic acid binding sites. The catalytic (primary) site, which also binds inhibitors such as oseltamivir carboxylate, is responsible for cleaving the sialic acid linkages that bind viral progeny to the host cell. |
|
Feb 27, 2020
by
Acs
Science & Medicine Blogs |
Go to Top